
Non-precious PFM (Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal) is a type of dental crown that combines a metal substructure with a porcelain outer layer. In contrast to precious metal PFM crowns, non-precious PFM crowns utilize non-precious metals such as nickel-chrome or cobalt-chrome. The metal substructure provides strength and stability,. Non-precious PFM crowns are widely used due to their cost-effectiveness. However, it's important to note that some individuals may have allergies to non-precious metal materials.
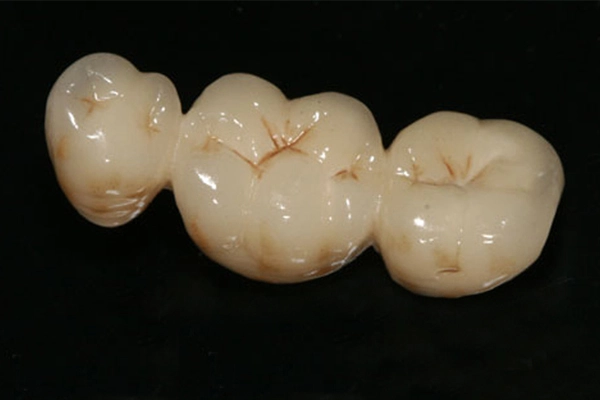
Semi-precious PFM (Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal) crowns combine a metal substructure with a porcelain exterior. Unlike non-precious PFM crowns, which use non-precious metals, semi-precious PFM crowns utilize higher-value metals like silver or other semi-precious metals. They offer both durability and aesthetic appeal, striking a balance between cost-effectiveness and a natural-looking smile. With enhanced biocompatibility and reduced risk of allergic reactions, semi-precious PFM crowns are a popular choice in restorative dentistry. Their superior strength and aesthetics make them a reliable option for patients seeking long-lasting dental restorations.

High Noble PFM (Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal) crowns combine a metal substructure with a porcelain outer layer. They use metals with a high noble metal content like gold, platinum, or palladium. These metals offer excellent biocompatibility, durability, and resistance to corrosion. The metal substructure provides strength, while the porcelain layer ensures natural aesthetics. High Noble PFM crowns are known for their superior fit, biocompatibility, and resistance to tarnish or discoloration. They are chosen for their high quality, longevity, and aesthetic results.
Porcelain Fused to Metal (PFM) is a popular dental restoration technique that combines the strength and durability of metal with the aesthetic benefits of porcelain. It is commonly used for dental crowns and fixed bridges, providing both functional and aesthetic improvements to the patient's smile.
PFM restorations can be categorized based on the composition of the metal alloy used within the framework. The three main types of PFM classifications are:

We are committed to providing high-quality service and support.
We are dedicated to assisting you and respecting your privacy.
As a dental lab from china, we look forward to engaging with you to meet your requirements and provide the best possible solution.
If you have any questions, needs, or concerns, please feel free to contact us.